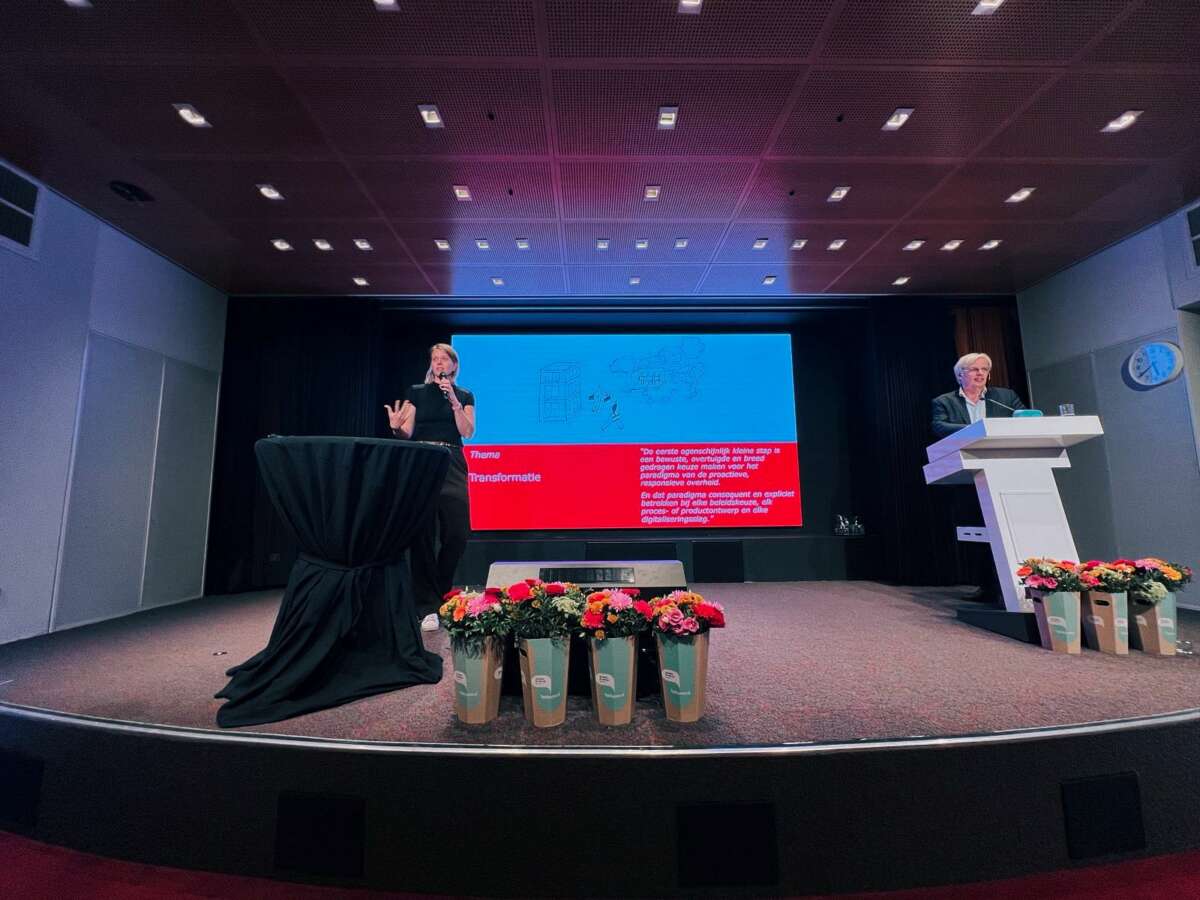
Crossing the Order is the latest book by Arre Zuurmond, government information management commissioner. During his book presentation (yesterday) he asked me to comment on the chapter Transformation. A great honor of course, you can read my speech below.
Want an update in your mailbox every month about my research? Then subscribe to my newsletter.
Fun things to do
When Arre asked me to comment today on the Transformation chapter of his new book, he said it was because “I was doing nice things.”
So I had to chuckle because I guess that is not what my director was thinking 8 years ago when he found out that I had been blogging for 2 years about what students thought about the loan system and how we as DUO could learn from their experiences and then what we should do differently.
That was not very board-sensitive of me.
Blogging is a way for me to think out loud, to make explicit things I don’t know or can’t do. To connect with others who can help me and thus learn more. In science, this is called reflection in action.
I often write about how we can be more reflective in government, alone and with citizens and colleagues. For example, in this blog: How to Reflect.
When I started as a utilization researcher in an implementation organization 10 years ago, this was a new job. We did not yet know exactly what it entailed and what to do with it in the organization. Feedback from citizens? While we just have our running systems and processes? What to do with that?
We don’t have an overview
In the beginning when I joined the government, I found it difficult to understand how the bureaucracy came together. It wasn’t until I went into schools, community centers, and talked to people dealing with government services that I understood how it came together. Or it didn’t.
In recent years, for example, I once walked with a bailiff, spent an entire afternoon sitting on a picnic bench in the library at an IDO where people can come by with issues about digital government, and listened to colleagues in call centers at DUO and the UWV.
I quickly noticed that there are few people in government who really have an overview of how the one is connected to the other. Who know why we actually have all these systems and information processes in place. As far as I’m concerned, this is the reason for the ever-expanding red tape that Arre mentions in his book.
I gained this insight during my master’s study on an Understanding Digital Government. You can read about it in the essay: We can’t be an understanding civil servant because we have lost the overview.
A chat in the neighborhood is the best way to find illogical bureaucracy in your organization. So my advice to anyone is always “go out of your office and have that chat with someone related to your service, product, policy, organization.”
Don’t know where to start? Here fixed 20 ways how to connect with your target audience.
How the government collects money
A good example of red tape is the current topic I am working on: how the government collects money from citizens. They all do that separately, as competitors of each other, with separate regulations, at separate speeds, and also with separate definitions and methods of how you calculate someone’s subsistence level, for example. And that works out disastrously for a lot of people in our country.
Only when you have that chat in the neighborhood with someone in that situation do you see that, because with blinders on from your own organization, it kind of seems to make sense.
What makes me very happy, then, is that for about 2 years now, the advice to have a chat is no longer met with a sigh. It is no longer a strange thought that you would do that, as it was 10 years ago.
And perhaps the biggest change is that people today consider me board-sensitive, even though I’m doing exactly the same thing I was doing 8 years ago. I still put all this stuff on my blog, where you are now reading this piece.
It tells me that this “new order” of Arre is closer than we might sometimes think.
Pracademic
With me, a lot of others in government are now learning along the way. I am now doing PhD research with TU Delft and 8 major implementers on how to design good digital services in government. Like Arre, I try to be a pracademic, a scientist from/in practice.
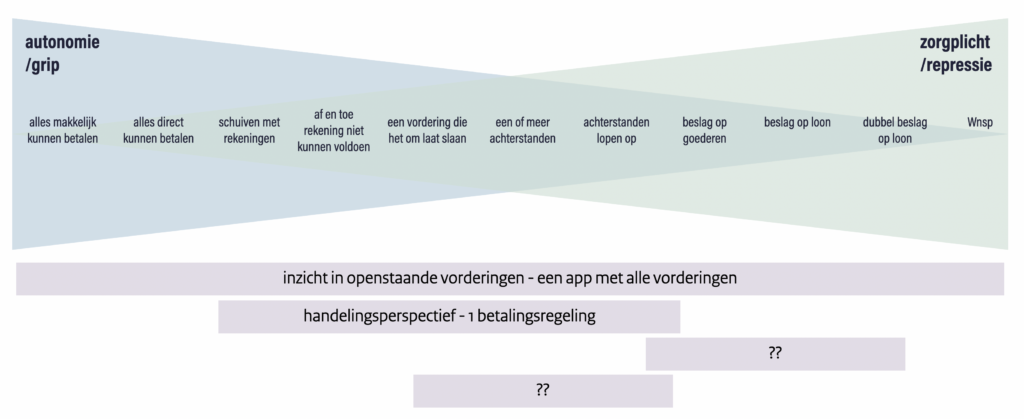
The guiding principles in my research are user engagement and iterative learning. For this research I am following for 2 years the program Clustering National Debt Collection where they are redesigning in this human-centered way how the government collects debt jointly with consideration for personal situations. Among other things, they create a debt overview for overview and insight and a joint payment scheme for citizens in arrears.
These are information services that are good for people.
Arre gives some drivers for change in government. He says that we have to make a conscious decision to work differently. That we have to think not in technology but in information and, I would add, relationship. And also, for example, that we just have to start somewhere. That’s great, because you can just do that in the place where you’re already sitting.
Cardinal virtues
Arre gives us a few cardinal virtues in his book: wisdom, justice, courage and moderation.
To that I would like to add 1. That is compassion. Understanding of each other.
Change is hard, and that’s okay.
When I was 14 I moved to the Netherlands and in a short time everything was suddenly different for me. I found that terrifying. I didn’t know the rules, the social codes and didn’t know the route in this new environment. Both figuratively and literally: I suddenly had to drive on the right instead of the left.
Just as Arre wants to flip bureaucracy, for me traffic was flipped.
I have lived in the Netherlands for 20 years now, but I still occasionally say, just before I want to drive away, “In the Netherlands we drive on the right.” This must not give my passengers much confidence and yet they always stay put.
Let’s have compassion for each other. Help each other find and learn the new rules, discover new routes, learn out loud, and thus navigate that “flipped bureaucracy” and arrive at the destination of a digital government that works for people.
A route guide
In addition to compassion, we also need concrete directions. What I needed at 14, we need now.
Someone to show you the way if you get lost, we now have Arre’s book for that. And examples of traffic situations and how to act then. Concrete examples with insights that you can also apply in other situations can help enormously in navigating together to that new destination.
So in addition to this speech, Arre has also asked me to develop such an example in the coming months. As an action perspective to his book for others in government. I think that’s super fun, and I’m going to enjoy doing that together with the team where I’m doing my research.
Learning from the Progress Chart Empire
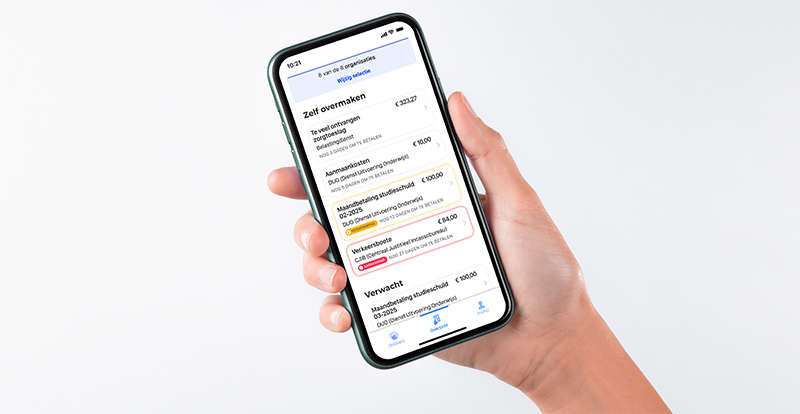
One of the services being developed in the program Clustering State Debt Collection is the State Claims Overview. This fall the Receivables Overview will become available to a first group of users and this will be expanded and further developed in the coming years.
In this Claims Overview, citizens can get an overview of the payment obligations they have outstanding with the government, and understand what this means for their situation. For example, what kind of payments are involved and what the term is. In the future, more and more action perspectives will be added. For example, a payment schedule for multiple claims at the same time, which can take into account your ability to pay and a pause button if you are in danger of going underwater.
This project is special in 4 ways, and we are going to make those lessons explicit in the coming months.
First, how you look at the relationship and interaction of citizens with government. In this particular case study, we put citizens on equal information status with the government. Citizens themselves request their data from the source, and the government does not have the total overview that citizens themselves have.
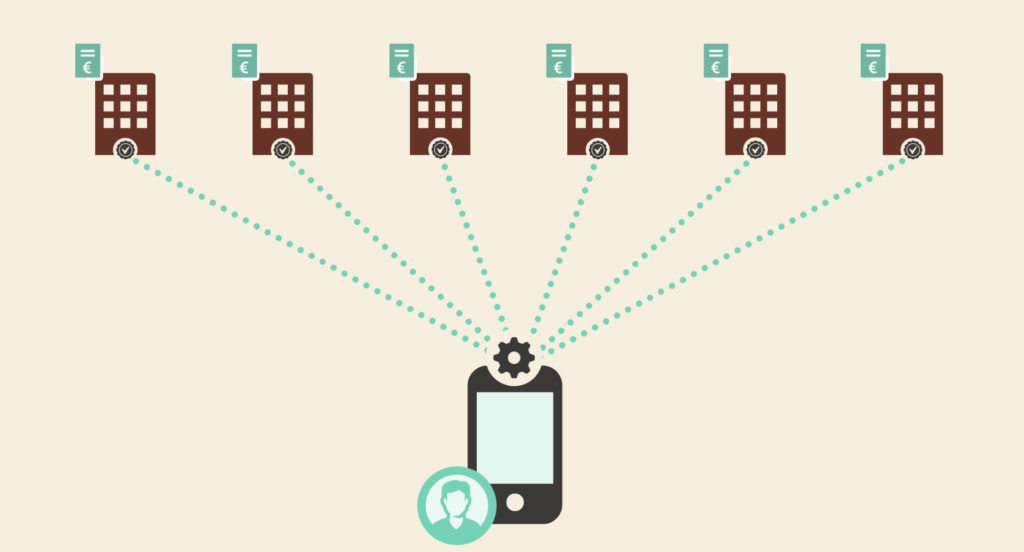
To this end, concrete technical standards are being developed that realize this interaction vision. Information between citizens and government will be exchanged with privacy by design as the starting point. This is the second point we are working on. These standards can also be applied in other projects.
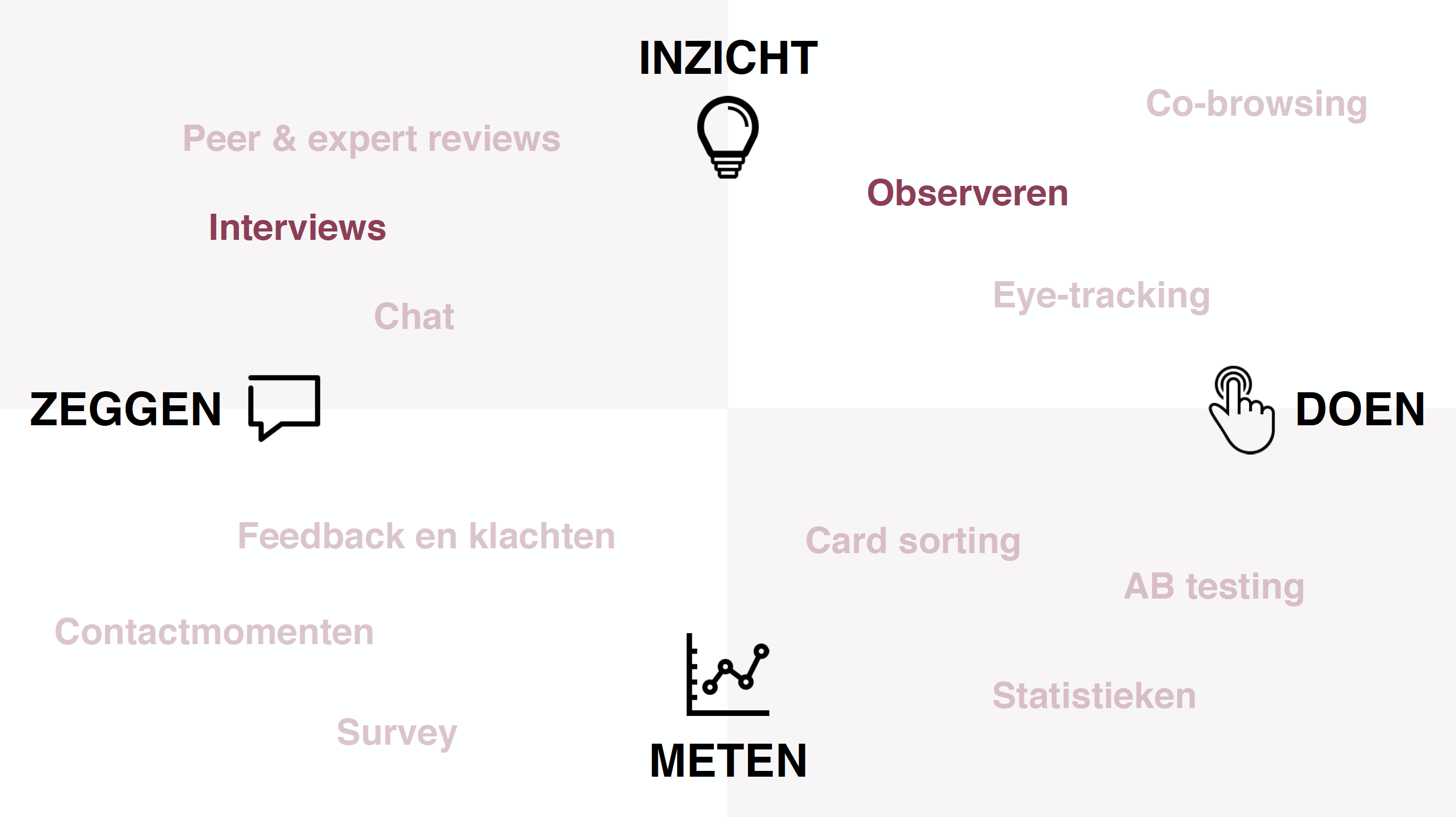
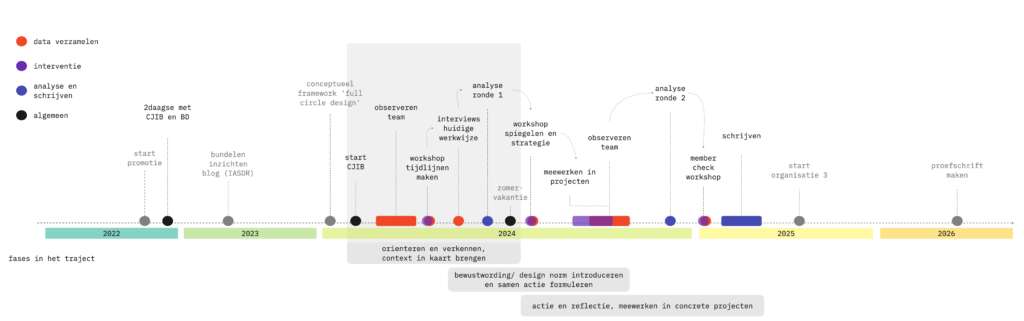
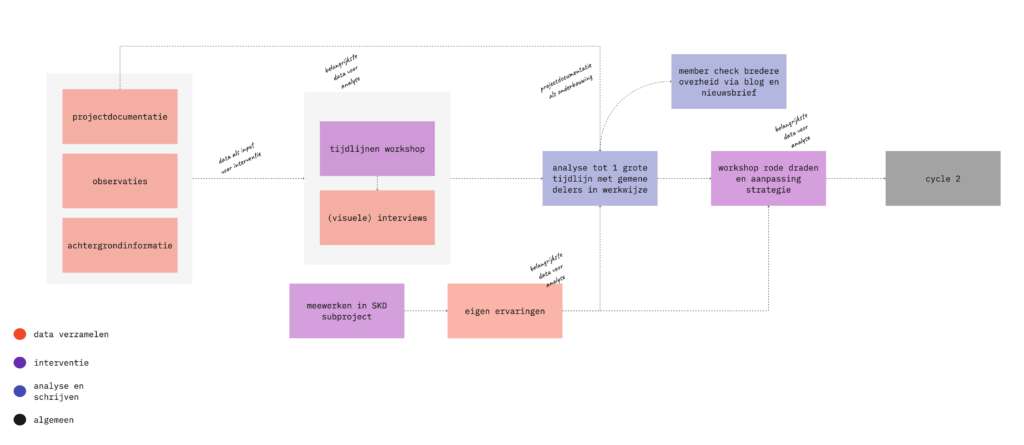
The third aspect is the methodology. The Progress Chart is developed iteratively, involving users at each step. The insights from the user research are shared publicly every sprint. Every 3 months there is a Grand Demo, where the team shows all stakeholders and interested parties what has been achieved in the previous quarter.

The fourth and final aspect: the Claims Review is a collaboration between all kinds of organizations. Actually it belongs to no one, yes, to the citizen, but the service belongs to all organizations together. That also means you need a new form of governance. Where do you manage the technical protocols, who deals with the connections and who deals with the quality of the interaction with the citizen?
What we want to create is a blueprint of these 4 points. I imagine a kind of traffic guide that we can use to navigate to Arre’s new order and what that means for how we look at the relationship citizen government, what we create next, how we do it and how we govern it.
Can’t wait for us to finish this? At vorijk.co.uk you can already browse through all the documentation, such as source code, usage studies, and general explanations of what the Progress Chart is all about and how it is made.
Continue reading
Arre Zuurmond’s book of course: Dwars door de orde. An unorthodox route to responsive government. Fresh off the press!
Platformland, by Richard Pope (2024). Excellent book on how to create the next generation of public services.
Good services by Lou Downe (2020). About, yes, the title says it all, what good services are. Soon they will also come out with the counterpart Bad Services, no doubt also a reading tip.
My blog, you’re already here. Browse the archives. And check out debegripvolleambtenaar.nl, my master’s thesis on an understanding digital government.
Want monthly updates in your mailbox about my doctoral research? Then subscribe to my newsletter.